Core Java第九章知识点总结——接口
知识点预览
接口的概念
接口的多继承
子类的多实现
使用接口的好处
接口的概念
1. 什么是接口
接口是特殊的抽象类
属性:公开 静态 常量
抽象类
方法:公开 抽象
2.interface关键字(abstract class)
a) 接口------编译------->.class文件
b) 特殊抽象类
publicstatic final
c) 可省略
public abstract
d) 接口:可声明引用,不能创建对象抽象类可定义构造方法,但接口不可,而且不会提供默认的。
3. implements关键字
a)实现接口--------->所有方法均实现
b) MyInterface m1 = new MyClass();
c) 接口的特点
i. 接口的继承
1. 接口之间继承:extends
package chp9.ex03;
/**
*
* 说明:本程序演示了接口的继承
*/
interface IA {
void m1();
}
interface IB extends IA{
void m2();
}
class MyClass implements IB{
public void m1(){
System.out.println("this is m1()");
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println("this is m2()");
}
}
public class TestInterface1 {
public static void main(String args){
MyClass m1 = new MyClass();
IA m2 = new MyClass();//多态的使用
IB m3 = new MyClass();//多态的使用
}
}
2.接口和多态密不可分
接口的多继承
package chp9.ex04;
/**
*
* 说明:本程序演示了接口的多继承
*/
interface IA {
void m1();
}
interface IB {
void m2();
}
interface IC extends IA,IB{
void m3();
}
class MyClass implements IC{
public void m1(){
System.out.println("this is m1()");
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println("this is m2()");
}
public void m3(){
System.out.println("this is m3()");
}
}
public class TestInterface1 {
public static void main(String args){
MyClass m1 = new MyClass();
IA m2 = new MyClass();
IB m3 = new MyClass();
IC m4 = new MyClass();
}
}
子类的多实现
1. 子类的多实现
2.子类的多实现的同时还可以继承一个父类
extends写在implements之前
class MyClass extends CCimplements IA,IB{
}
package chp9.ex06;
/**
*
* 说明:本程序演示了类的继承和多实现
*/
interface IA {
void m1();
}
interface IB {
void m2();
}
class CC{
void m3(){};
}
class MyClass extends CC implements IA,IB {
public void m1(){
System.out.println("this is m1()");
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println("this is m2()");
}
//方法的覆盖
public void m3(){
System.out.println("this is m3()");
}
}
public class TestInterface1 {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyClass m1 = new MyClass();
System.out.println(m1 instanceof IA);
System.out.println(m1 instanceof IB);
System.out.println(m1 instanceof CC);
}
}
使用接口的好处
1.增加程序的通用性
a) 声明引用时要使用接口类型
b) 方法的参数要什么成接口类型
c) 方法的返回值要声明成接口类型
2.接口实现了特殊的多继承
3.解耦合(最主要的作用)
通过接口把强耦合转化为弱耦合
无接口:
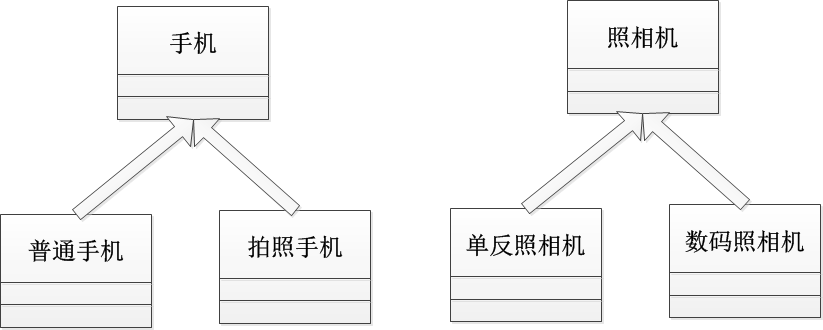
有接口:
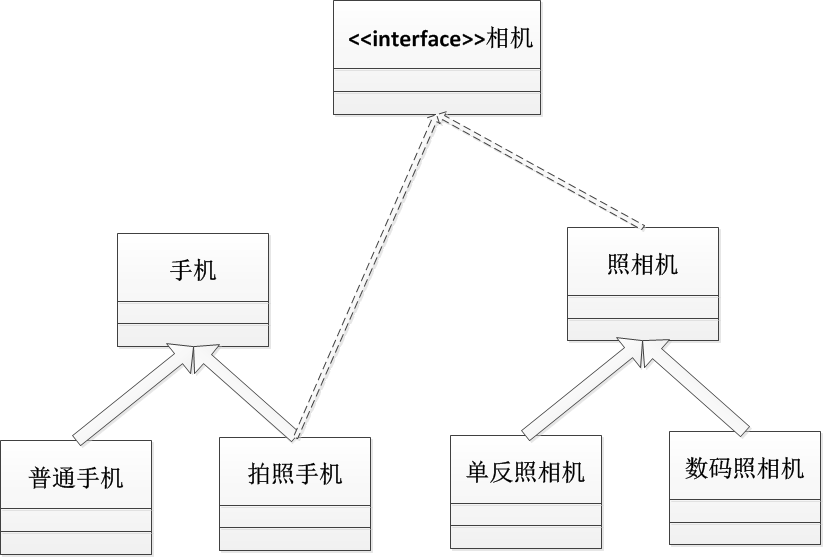
相机为什么不用抽象类:这样也造成了多继承
为什么手机不继承相机:普通手机也有照相功能
package chp9.ex07;
/**
*
* 说明:本程序演示了接口的好处——解耦合
*/
public class TestBuble {
public static void main(String args[]){
RedBuble red = new RedBuble();
GreenBuble green = new GreenBuble();
Lamp l = new Lamp();
l.setBuble(red);
l.on();
l.setBuble(green);
l.on();
}
}
interface Buble{
void light();
}
class RedBuble implements Buble{
public void light(){
System.out.println("red shine");
}
}
class GreenBuble implements Buble{
public void light(){
System.out.println("green shine");
}
}
class Lamp {
private Buble buble;
//安装灯泡的灯口
public void setBuble(Buble buble){
this.buble = buble;
}
//开灯
public void on(){
buble.light();
}
}
分享到:












相关推荐
Oracle工作总结——日志文件切换频率的调整 Oracle工作总结——日志文件切换频率的调整
oracle培训教材——备份与恢复以及常用命令 把oracle数据库从我的电脑上迁移到机房的电脑上,一开始采用dmp/imp方式,但是发现需要导出很多用户,太麻烦。所以决定采用冷备份/冷恢复的方式。
oracle内部培训资料——游标 实例代码,使用注意事项等
Oracle SOA 套件——Oracle BPEL 流程管理器Oracle SOA 套件——Oracle BPEL 流程管理器
Oracle学习笔记——day01 学习的好东西Oracle学习笔记——day01
Oracle学习笔记——day02 学习的好东西 Oracle学习笔记——day02
Oracle学习笔记——day04 学习的好东西 Oracle学习笔记——day04
Oracle学习笔记——day05 学习的好东西 Oracle学习笔记——day05
Oracle学习笔记——day03 学习的好东西 Oracle学习笔记——day03
Oracle数据库教程——nbu恢复oracle数据库案例
Oracle10g 培训——基础知识,适合初学者了解,
oracle系统培训课件——资料包(7个ppt).rar
Oracle数据库技术——动态SQL。详细资料~
很好的oracle 10培训资料——管理第二部分:管理实例
Oracle应用项目——使用OracleEM创建表空间.pdf 学习资料 复习资料 教学资源
Oracle数据库管理员培训教材——10g版本,学习初学oracle,oracle进阶等有很好的帮助,就是好!
Oracle工作总结——日志文件切换频率的调整.doc
Oracle大学培训资料——Oracle9i 数据库管理基础 I(中文版)
Oracle 数据库系统——基础与工具.pdf
CONFIGURING ORACLE GOLDENGATE ———— 28 STEP 1 PREPARE THE ENVIRONMENT————— 29 GOLDENGATE COMMAND INTERFACE————— 46 STEP 2 CHANGE CAPTURE 51 STEP 3 INITIAL LOAD———— 64 STEP 4 CHANGE ...